As we move back into the distant past the universe becomes
smaller, more dense, and much hotter.
With these extreme conditions the matter in the universe undergoes phase changes or phase transitions, similar to water.
Grand unification requires that all of the physical forces are the same immediately after the Big Bang. This grand unification can be expressed as a symmetry.
As the universe cooled after the big bang gravity was the first to "freeze" out and break symmetry, then the Strong force, and then the weak force. At very low temperatures we get the matter particles we know.
Topological Defects can form while the universe moves through phase transitions.
The defects are configurations of matter that retain the old symmetry or phase.
Cosmic strings are formed when axial or cylindrical symmetry is broken. These strings are trillion times smaller that the radius of an Hydrogen atom and may stretch
across the universe.
The evolution of the cosmic string includes three main processes
Cosmic expansion will cause the strings to become stretched out .
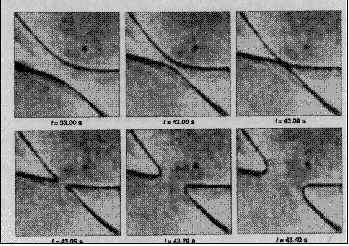
When two ends of strings cross each other they can intercommute and exchange ends. Intercommuting has been observed in nature in neumatic liquid crystals.
[11]
One string can also interact with its self to produce a loop
The strings and loops can radiate by vibrating and hence loose energy.
The result of these processes implies that the strings become more dilute as time and the universe expand.
Simulations are produced in order to study the cosmic strings and their evolution. The three processes mentioned are used in the simulations.
These simulations give an idea of how many cosmic strings are left, string velocity, and distance between them. This will aid in their detection.
With these extreme conditions the matter in the universe undergoes phase changes or phase transitions, similar to water.
Grand unification requires that all of the physical forces are the same immediately after the Big Bang. This grand unification can be expressed as a symmetry.
As the universe cooled after the big bang gravity was the first to "freeze" out and break symmetry, then the Strong force, and then the weak force. At very low temperatures we get the matter particles we know.
Topological Defects can form while the universe moves through phase transitions.
The defects are configurations of matter that retain the old symmetry or phase.
Cosmic strings are formed when axial or cylindrical symmetry is broken. These strings are trillion times smaller that the radius of an Hydrogen atom and may stretch
across the universe.
The evolution of the cosmic string includes three main processes
Cosmic expansion will cause the strings to become stretched out .
When two ends of strings cross each other they can intercommute and exchange ends. Intercommuting has been observed in nature in neumatic liquid crystals.

[11]
The strings and loops can radiate by vibrating and hence loose energy.
The result of these processes implies that the strings become more dilute as time and the universe expand.
Simulations are produced in order to study the cosmic strings and their evolution. The three processes mentioned are used in the simulations.
These simulations give an idea of how many cosmic strings are left, string velocity, and distance between them. This will aid in their detection.
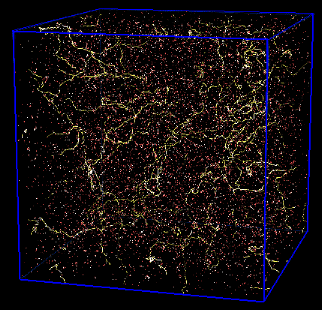 radiation dominated[11]
radiation dominated[11]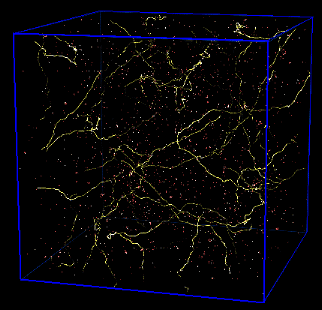 matter dominated [11]
matter dominated [11]