 Space Science News home |
|
| Mar. 9, 1999: "S" marks the spot for scientists trying to forecast solar eruptions that can damage satellites, disrupt communications networks and cause power outages. Using the Japanese Yohkoh spacecraft, NASA-sponsored scientists have discovered that an S-shaped structure often appears on the Sun in advance of a violent eruption, called a coronal mass ejection, that is as powerful as billions of nuclear explosions. Below: An example of three nearby sunspot groups showing non-sigmoid and sigmoid (non-S-shaped and S-shaped) magnetic configurations. Themiddle and right regions show clear sigmoidal patterns. The strongly S-shapedmiddle region later erupted, after this picture was taken. 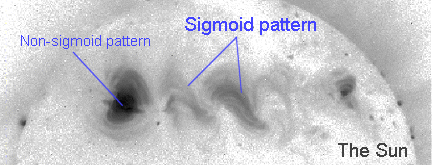
"S marks the spot," said Dr. Alphonse Sterling of Computational Physics, Inc., Fairfax, VA, detailed to the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS), Japan. "We have found a strong correlation between an S-shaped pattern on the Sun, called a sigmoid, and the likelihood that an ejection will occur from that region within days. Each sigmoid is like a loaded gun that we now know has a high probability of going off." |
 Sign up for our EXPRESS SCIENCE NEWS delivery | "The S-shaped regions are the dangerous ones," said Dr. Richard Canfield, a research professor of physics at Montana State University-Bozeman, and lead author on a paper to be published in the March 15 issue of Geophysical Research Letters. "As soon as we can recognize an S-shaped region, we know that it is more likely to erupt. Other common structures look like a butterfly, quite symmetric, and these rarely erupt." |
The sigmoid structures are likely the result of twisted solar magnetic fields, said Dr. Sarah Gibson of the University of Cambridge, UK. "The key to the coronal mass ejection is its magnetic field, which can structure and propel the mass outward," said Gibson. Right: This complex composite image of a coronal mass ejection - an expanding storm ofenergetic particles from the Sun - was constructed using data recorded by the SOHO spacecraft onNovember 6, 1997. Four images from two SOHO (Solar Orbiting Heliospheric Observatory) instrumentshave been nested to show the ultraviolet Sun at center and a large eruption of material from the right-handsolar limb. The picture covers a regionextending about 13.5 million miles from the Sun (32 Solar Radii). More information Right: This complex composite image of a coronal mass ejection - an expanding storm ofenergetic particles from the Sun - was constructed using data recorded by the SOHO spacecraft onNovember 6, 1997. Four images from two SOHO (Solar Orbiting Heliospheric Observatory) instrumentshave been nested to show the ultraviolet Sun at center and a large eruption of material from the right-handsolar limb. The picture covers a regionextending about 13.5 million miles from the Sun (32 Solar Radii). More informationCoronal mass ejections are violent discharges of electrically charged gas from the Sun's corona, or outer atmosphere. The largest explosions in the solar system, they hurl up to 10 billion tons of gas into space at speeds of one to two million miles an hour. The outbursts occur several times a day, but not all are hurled toward Earth. Images from various spacecraft have provided often spectacular images and information after a CME had already erupted, but scientists have been trying for some time to identify a precursor for these events. Sterling and Dr. Hugh Hudson of the Solar Physics Research Corporation, Tucson, AZ, working at ISAS, first observed a relationship between a sigmoid shape before a CME and a cusp or arcade shape afterwards. Later, Hudson and others found the same pattern in several other ejections. That finding prompted Canfield, Hudson and Dr. David McKenzie, a research scientist at Montana State University, to look for a statistical correlation between the sigmoid shape and subsequent eruptions. They viewed a total of two years of daily X-ray images from the Japanese/US/UK Soft X-ray Telescope on Yohkoh. The composite pictures -- 50 images each day -- were made into movies for analysis.  Left: The unusual banana-shaped loops shown above are actually part of acomputer-generated snap-shot of our Sun's magnetic field. This animated frame was constructed using datafrom the ground-based U.S. Solar Vector Magnetograph and the space-based Japanese X-Ray TelescopeYohkoh. Surfaces of constant magnetic field strength loop through the Sun's corona, break through theSun's surface, and connect regions of magnetic activity such as sunspots. More information Left: The unusual banana-shaped loops shown above are actually part of acomputer-generated snap-shot of our Sun's magnetic field. This animated frame was constructed using datafrom the ground-based U.S. Solar Vector Magnetograph and the space-based Japanese X-Ray TelescopeYohkoh. Surfaces of constant magnetic field strength loop through the Sun's corona, break through theSun's surface, and connect regions of magnetic activity such as sunspots. More information"We need to get past simple classifications such as, 'Is it sigmoidal or not, is the sunspot big or small,' and get to quantitative measurements that answer, 'how twisted are the magnetic fields, how big is the spot'," Canfield said. "As well, we want to know in which direction the ejection is going to go and how many regions are likely to erupt." Ultimately, Canfield continued, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) may be able to include warnings of coronal mass ejections in its space weather forecasts. NOAA is building a Solar X-ray Imager similar to that on Yohkoh, scheduled for launch next year, he said. |
| | |
| Solar Physics at Marshall Space Flight Center describes work here, including the Solar Vector Magnetograph which takes pictures of the solar magnetic field, and the GOES Soft X-ray Imager, managed by NASA/Marshall will provide minute-by-minute images of the solar corona.
| |
 Headlines Headlinesreturn to Space Science News Home
|